Type Casting / Type Conversion
Converting the values of one type to another for the evaluation of an
expression is called type casting or type conversion.
Type casting is of two types:-
1) Upcasting – Conversion of lower types to upper types is called upcasting. Upcasting is implicitly performed.
Upcasting is performed according to the following graph:-

Explanation -
a.
Let n be an
integer and n = 2n then to store n in memory in integer
representation k bits are required.
For e.g
32768 = 215
0 111111111111111
15 bits are required to store 32768.
b.
In floating
point representation number is not stored rather its exponent is stored.
i.e
32768 = 215
Then only 15 need to be stored.
n=2k and k = 2l where l<k then to store n only l
bits are required.
2) Downcasting – Conversion of higher types to lower type is called downcasting. Downcasting need to be explicitly performed.
Syntax –
(target type) expression;
Example- float f = 12.45; ==========> float f = (float)12.45; OR float f = 12.45f;
By this statement compiler
- PROGRAM – Rectangle.java
- public class Rectangle
- {
- private int l, b;
- public void Rectangle(int x, int y)
- {
- l = x;
- b = y;
- }
- public void display()
- {
- System.out.println("Length = " + l);
- System.out.println("Breadth = " + b);
- }
- public int area()
- {
- return l * b;
- }
- public void setDimension(int x, int y)
- {
- l = x;
- b = y;
- }
- }
- Syntax of creating object of a class-
- className ReferenceVariable = new className();
- OR
- className ReferenceVariable;
- ReferenceVariable = new className();
Reference Variable – is an implicit pointer that contains the reference of a class object. In Java, objects are dynamically created. Hence, they don’t have names. They are referred using the name of their reference variable.
In C++ :-
Rectangle r;

Traditionally in languages when we write statement
int a=5, b=6, c=10;
a table is created during compilation.
Variable Name
|
Type
|
Address
|
Value
|
Scope
|
a
|
int
|
0 + 1000
|
5
|
main
|
B
|
int
|
2 + 1000
|
6
|
main
|
c
|
int
|
4 + 1000
|
10
|
main
|
int * p;

Address & Reference denotes two different things.
o Address represents actual memory location whereas Reference represents a mechanism of finding out objects.
Different JRE provides different implementations of references.
o In Microsft JRE, References are implemented as pointers that is they actually holds the address of object.


o In Sun Microsystem JRE, Reference Variables are implemented as pointer to pointer.

In this implementation, Reference and Address are different.

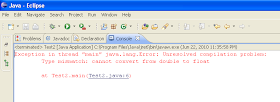
Now we will write a program RectTest.java to test the program Rectangle.java written above.
- public class RectTest
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
- r.l = 5;
- r.b = 7;
- r.setDimension(5, 4);
- System.out.println("Dimension of rectangle r ");
- r.display();
- System.out.println("Area of r = " + r.area());
- }
- }
Output –
Since variables l and b are declared private so we cannot access it from outside.
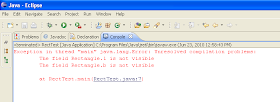
Now the same program RectTest.java again.
- PROGRAM RectTest.java
- public class RectTest
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
- //r.l = 5; // Invalid statement
- //r.b = 7; // Invalid statement
- r.setDimension(5, 4);
- System.out.println("Dimension of rectangle r ");
- r.display();
- System.out.println("Area of r = " + r.area());
- }
- }
OUTPUT –